Dog Tear Duct Anatomy

Tear stains on dogs are dark brown or reddish marks that appear under the eyes.
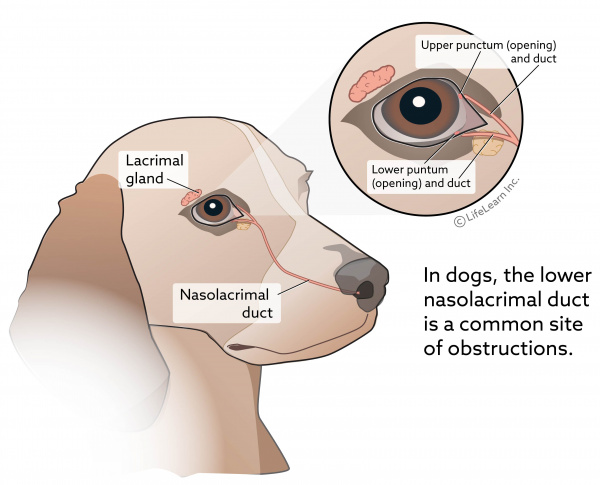
Dog tear duct anatomy. Therapy consists of surgically opening the blocked duct and keeping it open by inserting a tube or suture during healing. The nasolacrimal duct also called tear duct latin. Clinical signs include dampness beneath the eyes reddish brown staining of the fur beneath the eyes odor skin irritation and skin infection. Veterinary treatment is required.
Blocked tear ducts in dogs have a variety of causes including an eye infection scar tissue swelling or a lack of tear duct development. The lacrimal gland consists of orbital and palpebral parts that are continuous posterolaterally around the concave lateral edge of the aponeurosis of the levator palpebrae superioris muscle. The facial anatomy of brachycephalic breeds may play a role in this condition. At the medial canthus there are two entrances into the lacrimal drainage system the upper and lower puncta.
Epiphora or excessive tearing from the eyes can be a sign of tear duct blockage or more serious eye problems. You ll likely notice some epiphora or excess tearing as a sign of this condition along with staining around the eyes. Absence of the nasal tear duct openings at birth is known as imperforate lacrimal puncta. Drops may be added to the eyes to allow the pupils to become dilated so that the veterinarian may examine the internal parts of the eye using an ophthalmoscope.
The nasolacrimal duct is about 1 2 to 2 4 cm long it passes through the nasolacrimal canal which is formed by the lacrimal bone and maxilla and. The nasolacrimal tear duct may be flushed to evaluate the external parts of the eye. An incorrectly formed tear duct can also cause tear staining. This overflow of tears can lead to moisture and tear staining below the eye.
Ductus nasolacrimalis is a channel that is directly continuous with the lacrimal sac and opens into the nasal cavity forming the final part of the tear drainage system of the lacrimal apparatus. The lower nasolacrimal duct is most commonly affected and obstruction of the lower duct results in more clinically visible. The lacrimal gland latin. Previous upper respiratory tract infections.
In dogs b c of infection inflammation is there in the nasolacrimal duct we can clean by passing a small canula in the medial side of eye on both upper and lo. Mesocephalic and dolichocephalic dogs. In some dogs this nasolacrimal duct can become obstructed or blocked. This is an infrequent cause of watering eyes in young dogs.
Obstruction may result in tears overflowing and running out of the eye. The precorneal tear film flows over the cornea and conjunctiva into the medial canthal lake.